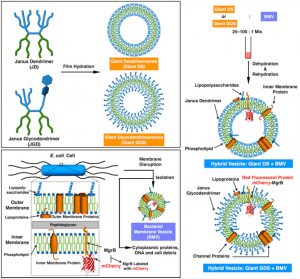
Illustration of the assembly of hybrid vesicles from artificial dendrimersome and natural E. Coli components.
D. A. Hammer, M. L. Klein, M. Goulian, V. Percec
Hybrid cell-like vesicles were prepared by coassembling (glyco)dendrimersomes with bacterial membrane vesicles (BMVs) derived from E. Coli. These assemblies incorporated transmembrane proteins such as the small fusion protein MgrB tagged with a red fluorescent protein, and glycoconjugates such as lipopolysaccharides and glycoproteins from E. Coli. In future work, coassembly of (glyco)dendrimersomes with mammalian including human cell membranes will be a focus with the goal of developing new systems for biomedical application.
Q. Xiao, S. S. Yadavalli, S. Zhang, S. E. Sherman, E. Fiorin, L. da Silva, D. A. Wilson, D. A. Hammer, S. André, H.-J. Gabius, M. L. Klein, M. Goulian, V. Percec. “Bioactive Cell-Like Hybrids Co-Assembled from (Glyco)Dendrimersomes with Bacterial Membranes.” Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 113, E1134–E1141(2016c). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1525589113
